Your PSA Level is High… Now What?
Chances are, you’ve heard the acronym “PSA.” It stands for prostate-specific antigen, a protein produced by cells in the prostate, which is a walnut-sized gland below the bladder that’s involved...
Read Article
Nearly All Vasectomized Men Are Candidates For Vas Reversal
In a large study of 1469 patients from multiple institutions, the success rate of a vasectomy reversal was inversely proportional to the obstructive interval. The shorter the interval, the higher the success rate. In men with obstructed intervals of less than 3 years, the likelihood of sperm present in the semen after reversal (patency rate) was 96%, and the pregnancy rate was 75%.
On the other hand, when the obstructed interval was greater than 15 years, the patency rate was 70%, and the pregnancy rate was 30%. Most men presenting to reversal have obstructed intervals between 3-14 years, the patency rate was 78%-87%, and the pregnancy rate was 44-53%. In interpreting this data, one should remember that the female partner’s age plays a very important role in the pregnancy and delivery rate.
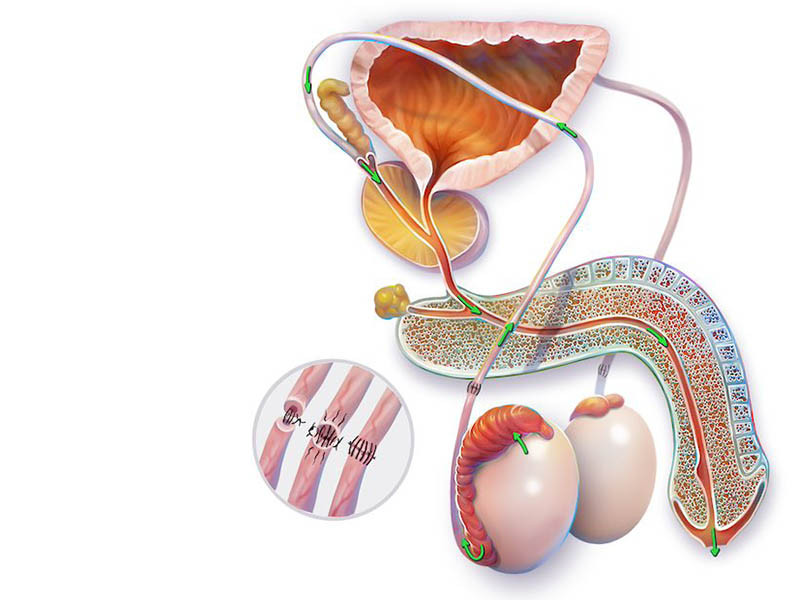
A Vasovasostomy or Vasectomy Reversal Procedure is a surgical procedure that is designed to bypass an obstruction in the male genital tract. Vasectomy is the leading cause of obstruction of the vas deferens, but men may be born with or acquire obstruction later in life from trauma or infection.
During a vasectomy, the vasa deferentia, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the seminal vesicles, are cut, tied, cauterized (burned or seared), or otherwise interrupted. A vasovasostomy creates an opening between the separated ends of each vas deferens so that the sperm may enter the semen before ejaculation.
The purpose of a VV or vasectomy reversal procedure is to restore a man’s fertility, and ultimate success is an unassisted pregnancy.
It is important to point out that the longer the obstructed interval, the higher the likelihood that a more complex reconstruction may be required. The operation is called the epididymovasostomy (EV). At the time of the surgery, it will be determined whether EV will be necessary. The success for epididymovasostomy is lower than for the standard vasectomy reversal.
Occlusion of the male reproductive duct is noted in 10-20% of all infertile men. It is very important for the diagnosis to be made since it is potentially correctable. The cause of ductal obstruction includes congenital absence or narrowing of the duct, scarring due to infection, and vasectomy.
The epididymis is the structure behind the testicle; it is made of coils of tiny tubules through which sperm migrate and mature. The procedure to correct epididymal obstruction is epididymovasostomy, during which the vas deferens are attached to an epididymal tubule to bypass the obstruction in between.
The patency rate for epididymovasostomy is about 50-60%, with a pregnancy rate of 30-40%. Some men may not have sperm present for up to 12 months after surgery. Pregnancy may take one to two years to achieve. Up to 10% of initially successful EVs may develop recurrent obstruction after sperm were initially present. We often recommend sperm banking as a safeguard against this problem.
Oral pain medication for 24-48 hours. Tylenol or Motrin may also be used. No heavy lifting, sports, or sexual activity should be engaged for 4 to 6 weeks. You may return to work in 7 days unless your job is physically demanding, then a 10-14 day wait is recommended. A semen analysis will be obtained at 3 months post-op. Sperm may not return for six months or more following VV or up to 12 months following EV.
Bleeding and infection are uncommon. Scarring and persistent pain at the operative site occur rarely.
The average length of time to achieve pregnancy is about one year. 3-5 % of initially successful VV may develop recurrent obstruction after sperm were initially present. It is recommended that you consider sperm banking once the sperm count has peaked to safeguard against this problem.
You may also consider the option of sperm harvest at the time of EV. In men whose procedures failed, the need for sperm remains. We can either collect sperm from the epididymal fluid or remove a small piece of the testis for sperm extraction. This sperm can then be used for IVF or be substituted later with ejaculated sperm. The advantage of ejaculated sperm is that much cheaper insemination may be feasible if the ejaculate contains sperm of sufficient quantity and quality.
A: With few exceptions, nearly all vasectomized men are candidates for microscopic reversal procedures, either a vas-vas (vasovasostomy, VV) or a vas-epididymis (epididymovasostomy, EV) connection may be performed. Couples with significant female fertility issues such as fallopian tube blockage or inadequate egg reserve should consider in vitro fertilization (IVF) since the restoration of normal sperm count may not overcome the co-existing female factor.
A: Four major factors are considered in advising individuals regarding the pregnancy rate following vasectomy reversal:
A: For routine reversal or VV, two one-inch incisions are made high in the scrotum. The amount of dissection is limited and you can almost equate the reversal to a “super-sized” vasectomy. The operative time is 2 to 3 hours. For more complicated reversal or EV, the incisions are longer to deliver the testes onto the operative field. A fair amount of tissue swelling is expected post-op. The operative time is 3 to 5 hours since epididymal exploration may be time consuming.
Recovery varies according to the procedure, routine VV is well tolerated with minimal narcotic requirement and one may return to a desk job in 3-5 days. EV is a bit more taxing, one should be prepared to rest for 7 days or more.
A: Sperm aspiration in conjunction with in vitro fertilization and sperm injection, IVF/ICSI, is an invaluable tool in the management of infertile couples. Sperm aspiration is done under local anesthesia with a butterfly needle to obtain viable sperm and is inexpensive; however, IVF/ICSI is not. Aspirated sperm are few in number and immature in function, fertilization requires these sperm to be individually injected into each egg in the laboratory. Pregnancy is then established following successful fertilization and embryo transfer to the uterus. Direct insemination is not possible with these sperm and has no role in the management of vasectomized men before reversal.
A: The rationale behind retrieving sperm at the time of reversal is to eliminate the need for future sperm aspiration for IVF if the reversal fails to produce sperm in the ejaculate. The sperm retrieved can only be used for IVF since only a small number of sperm are obtained.
Most men do not require sperm retrieval for the following reasons:
On the other hand, the case for retrieval can be made for those undergoing epididymo-vasostomy following extended obstructive interval since the patency will be significantly lower at 50-60%. In these men, we ask them to consider retrieval as an option; some insist on retrieval to avoid any future procedure while others have no problem with a “wait and see” approach.
Sperm may be retrieved by collecting the sperm containing vassal or epididymal fluid or by removing a small piece of testis tissue. The amount of testis removed is about 250 mg, about the size of 2-3 rice grains. It adds very little time to the procedure. Recovery is not much different than reversal.
Arrangements for sperm processing and storage must be made with the andrology lab before the procedure.
Call Georgia Urology today to schedule an appointment with one of our highly trained urologists to learn more about vasectomy reversal procedures.

Chances are, you’ve heard the acronym “PSA.” It stands for prostate-specific antigen, a protein produced by cells in the prostate, which is a walnut-sized gland below the bladder that’s involved...
Read Article
What we eat impacts every physiological process and anatomical structure, and the prostate is no exception. The foods we consume directly affect how the prostate functions. Lycopene has been on...
Read ArticleIs Low-Dose Daily Cialis/Tadalafil Effective in Treating Erectile Dysfunction/ED?
Cialis (Tadalafil) is best known as a treatment for erectile dysfunction, but it is also approved for benign prostatic hyperplasia...Read
Can Your Habits Help Prevent Bladder Cancer… Even if It Runs in the Family?
Bladder cancer doesn’t get as much airtime as other cancers, but it should. It’s the 10th most common cancer worldwide,...Read